Visual Search using Deep Learning (pt. 3) - Conclusion
This is the 4th and final part of Visual Search using Deep Learning. I highly recommend checking part 0, part 1 and part 2 before reading this post.
At this stage we have successfully trained a model that can embed images such that distance between embedding of visually similar images is small and the distance of embedding of visually dissimilar images is large.
Now, we will generate an embedding for all images in our catalogue. Code for generating embeddings is quite simple. This I will skip posting the same code again.
Embeddings shape for a subset of my dataset.
names1is array consisting of namepaths of the images.encoding1contains embeddings for the previously mentioned images.
print(names1.shape)
print(encoding1.shape)
(137317,)
(137280, 4096)
Computing nearest neighbor
Now to generate recommendations, we need to find other images in our dataset whose embeddings are at a small distance from embedding of given image.
neigh = NearestNeighbors(5,n_jobs=-1)
neigh.fit(encoding)
NearestNeighbors(algorithm='auto', leaf_size=30, metric='minkowski',
metric_params=None, n_jobs=-1, n_neighbors=5, p=2, radius=1.0)
Saving the model.
"""
Save Nearest Neighbor model object
"""
# joblib.dump(neigh, model_path+'nn_mtshirt.pkl')
"""
Load Nearest Neighbor model object
"""
neigh = joblib.load(model_path+'nn_mtshirt.pkl')
Now we will find nearest neighbor for all images in the dataset.
file = open("results_mtshirt","a")
for i in tqdm(range(int(137280/100))):
c = neigh.kneighbors(encoding1[i*100:(i+1)*100], 10, return_distance=False)
t = ""
for a in c:
for i in a:
t= t+str(i)+"\t"
t = t+"\n"
file.write(t)
file.close()
52%|█████▏ | 718/1372 [3:49:56<3:28:26, 19.12s/it] <br> Sample output <br>
# %timeit c = neigh.kneighbors(encoding1[100:110], 10, return_distance=False)
# print(t)
100 63224 16260 42554 17549 59820 73586 125306 122035 115010
101 75406 70201 82771 117563 119667 51405 133667 5979 96449
102 73952 103936 77570 1505 34074 26714 125377 36586 130659
103 50453 11533 88831 45600 11997 128065 67361 67496 27089
104 113559 17717 38480 97309 19264 3914 2309 84518 88550
105 66126 36091 128527 39117 125919 122481 44133 132392 130074
106 40671 72583 123225 120801 56280 104665 52862 69204 65332
107 55736 49595 84281 39546 7113 80444 18963 108602 102513
108 49159 47182 32244 47495 129107 82115 49216 82738 136818
109 102283 106145 78651 75553 32166 23820 109334 78924 40682
110 23012 123944 75373 65893 58203 107466 77792 34084 21356
My output
Now I will show some of the particulrly good examples of my model. I haven’t formatted the output pretty well so all suggestions will occur one after the other.
check = [i for i in range(10,15)]
for i in check:
print("******************************************")
b = Image.open(path+"images/men-tshirts/"+names[i])
plt.imshow(b)
plt.show()
c = neigh.kneighbors([encoding[i]], 10, return_distance=False)
for k in range(5):
# print(c[0][k])
b = Image.open(path+"images/men-tshirts/"+names[c[0][k]])
plt.imshow(b)
plt.show()






























The GOOD
See below some of the particularly good examples.
check = [0,1,15,9,11,18,23,24,29,35,42,47,52]
for i in check:
print("******************************************")
c = neigh.kneighbors([encoding[i]], 5, return_distance=False)
for k in range(5):
b = Image.open(path+"images/tops-and-tees-menu/"+names[c[0][k]])
plt.imshow(b)
plt.show()
******************************************


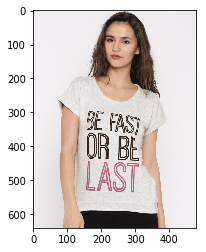






























































The BAD
See below some of the particularly icorrect recommendations.
#good 1,15,9,11,18,23,24,29,35,42,47,52
#fail 31,41
check = [31,41]
for i in check:
print("******************************************")
c = neigh.kneighbors([encoding[i]], 5, return_distance=False)
for k in range(5):
b = Image.open(path+"images/tops-and-tees-menu/"+names[c[0][k]])
plt.imshow(b)
plt.show()
******************************************










Quick drawbacks of current solution
Some of the readily observed issues in the recommendation model are :
- The embedding sometimes encodes the model’s face as a feature. Thus, in some cases suggestions for an item is some other random item worn by the same model.
- Similarly, the embedding seems to encode the pose of a model and makes suggestions accordingly.
- The embedding also seems to embed background patterns which also leads to incorrect suggestions.
Many of these issues can be resolved by preprocessing the image ie. zooming in on the apparel and removing background details like model face & pose.
Conclusion
Over this 4 part series on Visual Search using Deep Learning, I have tried to explain my workflow and share my implementation details. I hope you found this helpful and are able to successfully implement this or a better solution for your application. Let me know in the comments about your interesting application or solution to visual search. See you in another post. Bye!